SaaS Product Lifecycle Stages and Development Best Practices

You built a great product, but users aren’t sticking. Your team’s shipping fast, but features miss the mark. Sound familiar?
That’s the silent killer in SaaS—an unstructured product lifecycle. Without a clear, strategic framework guiding each stage—from idea to growth—you risk wasted development, misaligned teams, and customer churn.
This guide breaks down the SaaS product lifecycle into actionable stages, showing you how to:
Prioritize the right features
Validate fast with users
Align product, marketing, and sales
And scale with confidence
Whether you’re launching v1 or trying to fix a leaky product funnel, this roadmap helps you build SaaS that doesn’t just work—it wins.
What Is the SaaS Product Lifecycle?

The SaaS product lifecycle refers to the series of stages a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) product goes through from its initial conception to eventual decline or reinvention. This framework helps product teams and business leaders understand where their product stands, what challenges to expect, and how to plan for growth and sustainability.
Unlike traditional software and the traditional software development process, SaaS products operate on a subscription model, with continuous updates and user engagement being critical to cost savings and success. This makes the software development lifecycle management, including the product development lifecycle, especially important—not just for development, but for marketing, customer retention, and scaling in the fast-paced world of SaaS.
Key Stages of the SaaS Product Lifecycle:
Development: This is the planning and building phase. It involves market research, identifying a customer pain point, and developing a minimum viable product (MVP) to obtain early feedback, including new features. The goal is to validate the idea before investing heavily in features or infrastructure.
Introduction: The product is launched to the market. Early adopters begin using it, and feedback is crucial. The focus here is on achieving product-market fit, generating initial traction, and fine-tuning the offering.
Growth: With product-market fit established, the focus shifts to scaling. Teams invest in marketing, sales, onboarding, and customer support. Usage grows rapidly, and revenue starts to climb. However, competition also increases during this phase.
Maturity: Growth begins to slow as the market becomes saturated. The product is stable and widely adopted, but innovation may stall. Companies must focus on retention, customer success, cost optimization, and incremental improvements to stay competitive.
Decline or Renewal: If the product doesn’t evolve, it risks becoming obsolete due to changing customer needs or new competitors. Some companies choose to sunset the product; others pivot, rebrand, or release major updates to restart the cycle.
Why It Matters
Understanding the SaaS product lifecycle allows teams to:
Allocate resources more efficiently.
Time marketing and product development efforts strategically.
Reduce churn and improve customer satisfaction.
Innovate before competitors force change.
Lifecycle awareness isn’t just about knowing what stage you're in—it's about proactively managing transitions between stages to ensure long-term success.
How to Prepare for SaaS Product Development?
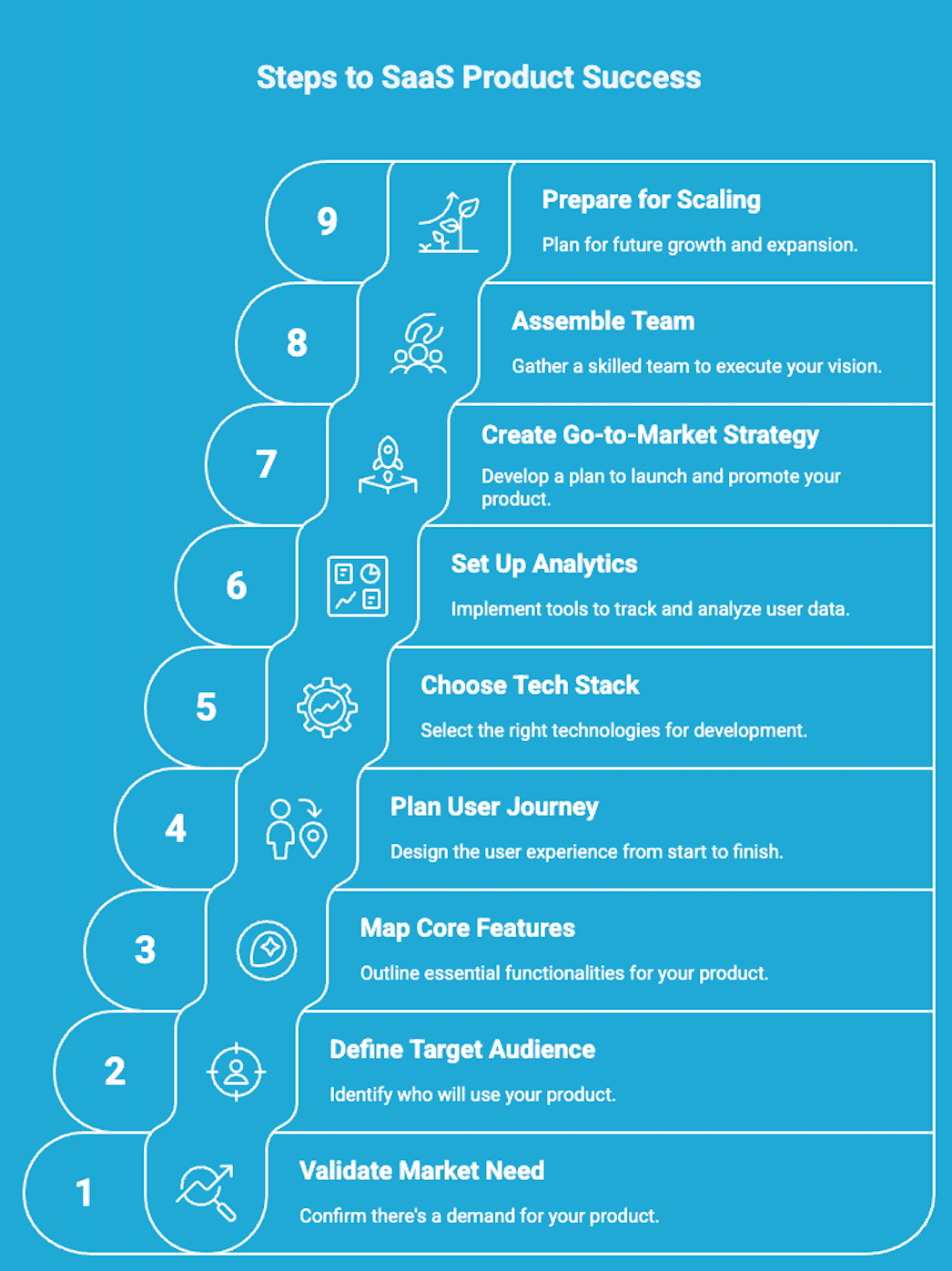
Building a SaaS product is more than just writing code—it’s about solving a real problem, creating something scalable, and setting up the systems that will support long-term growth. Whether you're a startup founder or a product lead, proper preparation can make or break your SaaS development journey. From confusion to conversion , here's how to prepare for product development.
1. Validate the Problem and Market
Before you start building, make sure the problem you're solving actually exists and is painful enough that people are willing to pay for a solution. Conduct user interviews, run surveys, analyze online forums, and study existing competitors to identify clear market gaps.
2. Define Your Target Audience
Be specific about who your product is for. Create buyer personas to understand user needs, motivations, and pain points. This clarity shapes your feature set, pricing, and messaging.
3. Map Out Your Core Features (MVP)
Focus on building a Minimum Viable Product—something simple that solves one core product idea exceptionally well. Avoid feature bloat. List out essential features only and prioritize based on user needs and development effort.
4. Plan the User Journey
Sketch out how users will move through your product from signup to success. A seamless onboarding experience and intuitive UI/UX are critical in reducing churn and driving adoption.
5. Choose the Right Tech Stack
Select technologies based on your scalability goals, budget, and team expertise. Consider long-term maintenance, performance, and integration capabilities.
6. Set Up Analytics and Feedback Loops
Decide early how you’ll track product usage, user behavior, and key performance metrics. Set up tools for analytics, user feedback, and A/B testing before launch to inform continuous improvement.
7. Create a Go-to-Market Strategy
The next step is to create a go-to-market strategy. Know how you’ll acquire your first users. Define your pricing model, marketing channels, and customer support structure. Whether you start with a freemium offer, free trial, or direct sales, plan it in advance.
8. Assemble the Right Team
You’ll need a mix of developers, designers, marketers, and customer support. Even in small teams, clarity of roles and alignment on vision is critical.
9. Prepare for Scaling
Even if you’re starting small, design your infrastructure, codebase, and support systems to handle growth. Think about version control, documentation, security, and performance from day one.
5 Stages of SaaS Product Lifecycle That You Need To Know About
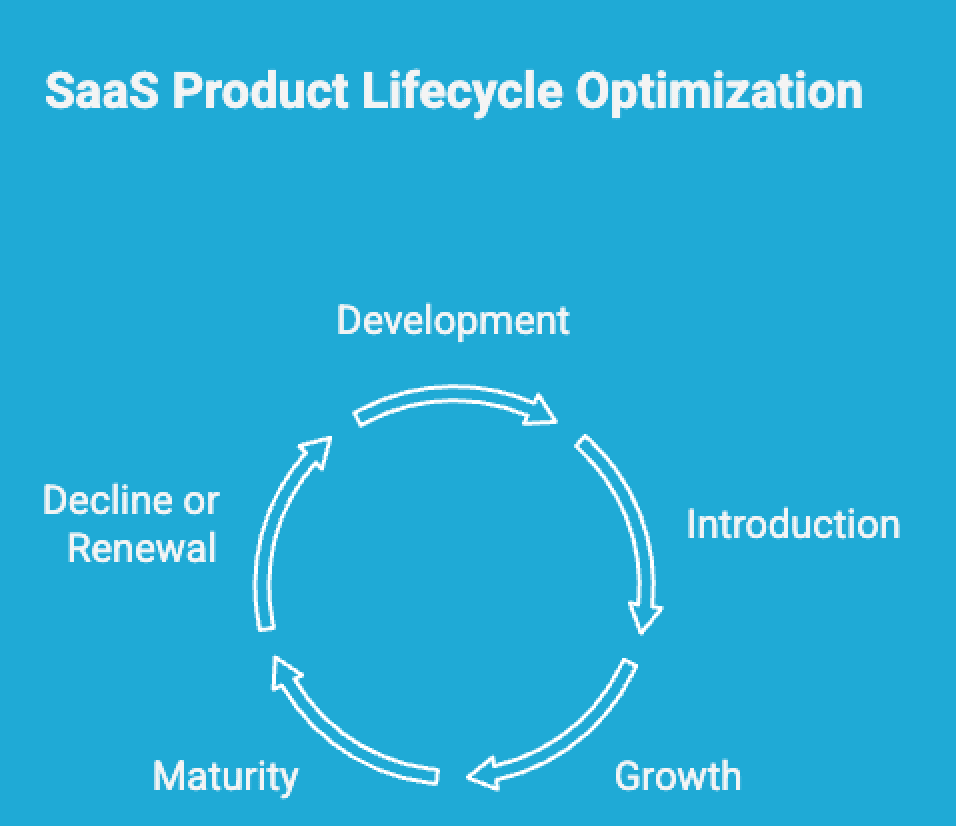
Optimizing your SaaS development lifecycle requires a strategic approach at every stage—from initial development to eventual renewal or phase-out. Each phase presents opportunities to improve product value, customer satisfaction, and long-term profitability. Here’s how to approach each one in the SaaS market for business growth.
1. Development Stage: Build with Purpose
This is where your SaaS product is born—not just in code, but in concept. Start by deeply understanding the problem you aim to solve through direct customer research. Identify specific pain points and validate them with your target audience before writing a single line of code.
Once you’ve confirmed a clear need, define a unique value proposition that will guide every development and messaging decision. From there, build a minimum viable product (MVP) that includes only the essential features necessary to test your core assumptions. Keep it lean, launch quickly, and use the feedback loop to drive smart iterations.
2. Introduction Stage: Prove Product-Market Fit
With your MVP in hand, the next step is to find your early champions. Focus on targeted outreach, beta programs, and partnerships that attract users who closely match your ideal customer profile. Their feedback is gold. Use it to refine your core features, eliminate friction, and enhance usability.
Simultaneously, start tracking metrics like engagement, retention, and churn to assess whether your product truly fits the market need. This stage is all about learning fast, adapting quickly, and confirming that people not only want your SaaS product but will keep using it.
3. Growth Stage: Scale Strategically
Now that product-market fit is in sight, it’s time to scale—but with intention. Double down on the acquisition channels that showed the most promise during the introduction stage, whether that’s SEO, paid ads, affiliate partnerships, or outbound sales.
As user volume increases, strengthen your customer support infrastructure with tools like knowledge bases, chatbots, or in-app messaging to maintain satisfaction. Additionally, revisit your pricing model to attract a larger user base. Small tweaks to tiers, trial periods, or feature access can significantly impact revenue while ensuring your offering remains competitive and valuable.
4. Maturity Stage: Maximize Retention and Efficiency
In maturity, your product has a stable customer base and predictable revenue. The focus shifts toward retaining users and improving margins. Invest in customer success programs that ensure ongoing value—things like onboarding sessions, training resources, and proactive check-ins.
At the same time, consider introducing advanced features or integrations that solve more complex use cases and deepen engagement on a cloud computing platform. Internally, this is the right moment to streamline operations—optimize infrastructure, reduce technical debt, and refine workflows to maintain profitability without sacrificing quality.
5. Decline or Renewal Stage: Decide the Future
Every product eventually reaches a crossroads: evolve or exit. Begin by evaluating your product’s relevance in the current market—are you still solving a real, pressing problem? If not, it might be time to sunset the product.
On the other hand, if customer interest persists but growth has stagnated, explore reinvention options such as major updates, rebranding, or pivoting to a new use case. Whatever direction you choose, ground it in user feedback. Understanding what customers want—or why they’re leaving—will help ensure your next move is both strategic and sustainable.
Who Is Part of The Product Development Team?
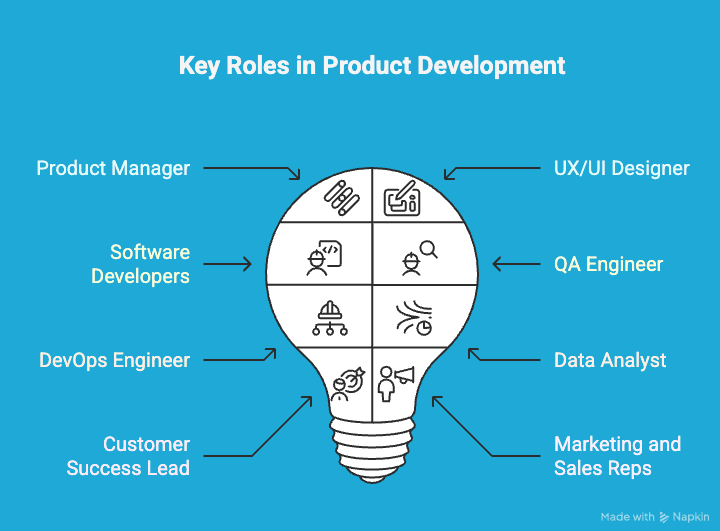
A typical SaaS product development team includes a mix of technical, strategic, and user-focused roles. Here’s who’s usually involved as a team members in SaaS development process:
1. Product Manager
Leads the product vision, prioritizes features, and aligns the team with business goals. Acts as the bridge between stakeholders and the development team.
2. UX/UI Designer
Designs user experiences and interfaces. Ensures the product is intuitive, visually appealing, and meets user expectations.
3. Software Developers
Build and maintain the product. This includes:
Frontend Developers – Focus on the user interface.
Backend Developers – Handle servers, databases, and application logic.
Full-Stack Developers – Cover both frontend and backend responsibilities to full potential.
4. QA Engineer (Quality Assurance)
Tests the product for bugs, usability issues, and performance problems. Ensures releases meet quality standards.
5. DevOps Engineer
Manages deployment, infrastructure, and continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD). Ensures scalability and reliability.
6. Data Analyst or Data Scientist
Analyzes user behavior and product performance data. Provides insights that inform feature improvements and business decisions.
7. Customer Success or Support Lead
Brings in feedback from users, helps with onboarding, and ensures customers are getting value from the product.
8. Marketing and Sales Reps (as needed)
While not part of the core build team, they offer insights on user demand, positioning, and feature messaging—especially during launch and growth stages.
Transform Your Sales with SmartCue: Personalized, Interactive Demos That Convert
Struggling to keep prospects engaged during product demos? Static, one-size-fits-all presentations often fail to show real value—and sales teams lose deals because of it.
SmartCue changes that with its SaaS solution. It lets you create personalized, interactive demos that speak directly to each prospect’s needs. Instead of just showing features, SmartCue helps you tell a story—one tailored to your buyer’s pain points and workflows.
With SmartCue, sales teams can embed demos into outreach, websites, or follow-ups, letting prospects explore the product at their own pace. The result? Better engagement, faster sales cycles, and more conversions.
You also get data-backed insights into how each demo performs, so your team can refine messaging and prioritize the right leads.
If you want to close more deals and cut the fluff from your demo process, book a 14-day free trial with us now. Let your product sell itself—with SmartCue.
Conclusion
To build a successful SaaS app product within the SaaS ecosystem, every stage of development needs a clear focus on the target market—from planning to the final stage of scaling, ideally with the involvement of project managers. Prioritizing user experience and the ease of use while aligning with business goals keeps growth sustainable.
Listening to feedback, researching the market, and analyzing user data helps you refine your product continuously. These insights show you what’s working, what’s not, and where to improve.
When you optimize every part of your SaaS lifecycle, you’re not just keeping up with the market—you’re staying ahead of it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the first step in optimizing a SaaS product lifecycle?
Begin with in-depth market research. Understand customer pain points, study competitors, and follow industry trends. This ensures your product is built to meet real demand and sets a strong foundation for development and testing.
How can small businesses effectively manage their SaaS products?
Leverage project management tools and automation to streamline workflows. Encourage regular team collaboration and use customer feedback to guide improvements. Tracking key metrics helps maintain product quality and support growth.
What are the common pitfalls in SaaS product development?
Frequent mistakes include ignoring user feedback, building without scalability in mind, and neglecting UI/UX design. Skipping thorough testing often results in bugs and churn, costing time and customer trust.
Can you optimize a SaaS product lifecycle without technical expertise?
Yes. Collaborate with skilled teams, use no-code or low-code tools, and focus on user feedback to guide decisions. With the right support and data, you can drive meaningful improvements without deep technical skills.
Comments
Your comment has been submitted